Have you ever noticed some Google search results look more detailed than others?
Some results show star ratings, FAQs, event dates, or even a recipe’s cooking time , all right there on the search page, before you even click the link. That extra information is not magic. It is schema markup doing its job.
If you are learning digital marketing or just starting to explore SEO, schema markup is one of those topics that sounds technical at first but is actually quite simple once you understand what it does.
In this blog, we break down exactly what schema markup is, why it matters for SEO, the different types, and how you can start using it all in plain, simple language.
Key Points At A Glance
- Schema markup is code added to your website to help Google understand your content better.
- It helps your website appear as rich results in Google search with ratings, FAQs, prices, and more.
- Schema does not directly improve rankings, but it significantly improves how your listing looks.
- Better-looking results get more clicks — which indirectly helps your SEO.
- There are different types of schema for different types of content.
- You do not need to be a developer to add schema to your website.
What Is Schema Markup?
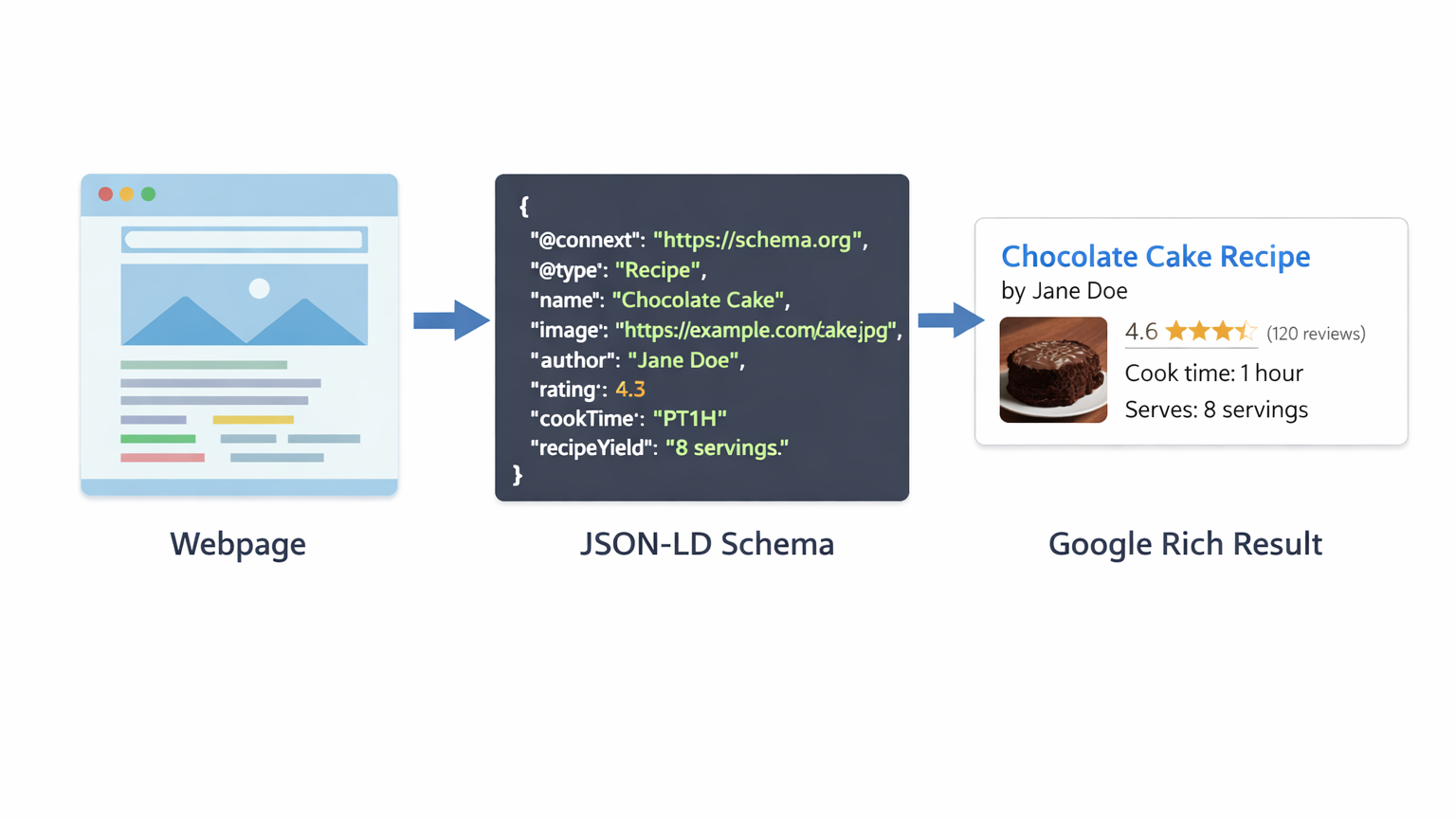
Schema markup (also called structured data) is a type of code that you add to your website to give search engines more context about your content.
Think of it like this. When you read an article, you understand the difference between a product review, a recipe, and a job listing. But Google is a machine it needs a bit of extra help to understand what type of content it is reading.
Schema markup is that help. It tells Google things like:
- This page is about a product – here is the price, availability, and rating.
- This page contains an FAQ – here are the questions and answers.
- This page is about an event – here is the date, time, and location.
Schema markup uses a standardised vocabulary from Schema.org, which is a collaboration between Google, Bing, Yahoo, and Yandex. When you use schema, you are speaking a language all major search engines understand.
Why Does Schema Markup Matter for SEO?
Schema markup matters because it unlocks rich results also called rich snippets in Google search.
A regular search result shows a blue link, a URL, and a short description. A rich result shows much more — star ratings, images, prices, step-by-step instructions, FAQs, and more. These results are larger, more eye-catching, and more informative.
| Regular Search Result | Rich Result with Schema |
|---|---|
| Plain blue title link | Title + star rating + review count |
| Generic meta description | FAQ dropdowns or event date shown |
| No visual elements | Product image, price, availability |
| Same size as every other result | Larger, stands out on the page |
Studies show that rich results consistently get higher click-through rates than plain results. More clicks mean more traffic — and more traffic signals to Google that your content is valuable.
So while schema does not directly change your ranking position, it makes your listing more attractive, which brings in more visitors — and that indirectly supports better rankings over time.
If you want to understand how SEO and structured data work together at a deeper level, the digital marketing course at Prodigiter covers schema, technical SEO, and much more in a practical, hands-on way.
Common Types of Schema Markup

Schema.org lists hundreds of schema types, but here are the most commonly used ones that are relevant for most businesses and marketers:
1. Article Schema
Used for: Blog posts, news articles, editorial content.
What it does: Tells Google the article’s title, author, publish date, and content type. This is especially useful for blogs and news websites that want their articles to appear in Google News or with a clear publication date.
2. Product Schema
Used for: E-commerce product pages.
What it does: Displays price, availability (in stock or out of stock), and star ratings directly in search results. This is a game-changer for online stores because it gives shoppers key information before they even visit the site.
3. FAQ Schema
Used for: Pages with a list of frequently asked questions.
What it does: Expands your search result to show individual questions and answers as dropdown items. This dramatically increases the size of your search listing and can double or even triple the space your result takes up on the page.
4. Review / Rating Schema
Used for: Product reviews, service reviews, local business reviews.
What it does: Shows the famous gold star ratings in search results. These are among the most powerful trust signals in search — users consistently click on results with visible ratings over plain text links.
5. Local Business Schema
Used for: Local shops, clinics, restaurants, agencies, and any location-based business.
What it does: Provides Google with structured information about your business — including name, address, phone number, opening hours, and geographic location. This strengthens your local SEO and helps you appear in map results.
To understand how this connects with broader local SEO strategies, read our blog on On-Page vs Off-Page SEO: What’s the Real Difference and Why Does It Matter? — it covers how on-site and off-site signals work together.
6. Event Schema
Used for: Webinars, workshops, concerts, conferences.
What it does: Shows the event name, date, time, and location in search results. If you run training events or live sessions, event schema makes your listing significantly more informative and click-worthy.
7. Course Schema
Used for: Online or offline educational courses.
What it does: Displays course name, provider, and description in search results — ideal for educational institutions and training centres. This is especially relevant for anyone in the ed-tech or digital marketing training space.
How Is Schema Markup Added to a Website?
There are three formats used to write schema markup JSON-LD, Microdata, and RDFa. Google recommends JSON-LD, and it is the easiest to implement.
JSON-LD is a small block of code that sits in the head section of your webpage. It does not affect how the page looks to visitors at all it only communicates with search engines behind the scenes.
Ways to Add Schema Without Being a Developer
- Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper: A free tool where you highlight content on your page and Google generates the schema code for you.
- WordPress Plugins: Plugins like Yoast SEO, RankMath, and Schema Pro let you add schema through a simple settings panel no coding needed.
- Google Tag Manager: For more advanced users, you can inject schema code via GTM without touching the website files directly.
Once added, always test your schema using Google’s Rich Results Test tool. It tells you whether your markup is valid and which rich results your page is eligible for.
Common Schema Markup Mistakes to Avoid
- Marking up content that is not visible on the page Google considers this spammy.
- Using the wrong schema type for your content always match the schema to what the page is actually about.
- Adding schema but never testing it always validate with Google’s Rich Results Test.
- Expecting schema to instantly boost rankings it improves visibility and CTR, not position directly.
- Adding fake ratings or misleading information in schema this can result in a manual penalty from Google.
Final Thoughts
Schema markup is one of those SEO elements that many businesses overlook — but the ones who use it correctly gain a real, visible advantage in search results.
It will not make a poorly written page rank on page one. But it will make a well-optimised page stand out far more than a competitor’s plain result — leading to more clicks, more traffic, and more trust.
Schema markup is one of those topics that separates a good digital marketer from a great one. Most people learn SEO at a surface level — keywords, content, backlinks. But the ones who understand technical elements like schema, Core Web Vitals, and structured data consistently outperform those who don’t.
If you are serious about building a career in digital marketing and want to learn these skills hands-on — not just in theory explore the Advanced Digital Marketing Course at Prodigiter. It is designed to make you genuinely job-ready, trained inside a real agency environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Does schema markup directly improve my Google rankings?
Not directly. Schema does not change your ranking position on its own. However, it improves how your search result looks, which increases click-through rates. Higher CTR sends positive signals to Google and can support better rankings over time.
2. Do I need to know coding to add schema markup?
Not necessarily. Tools like Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper and WordPress plugins like RankMath or Yoast SEO allow you to add schema without writing code. However, understanding the basics of JSON-LD is helpful for customisation.
3. Which schema type should I use for my business?
It depends on your business type. Local businesses should use Local Business schema. E-commerce stores benefit most from Product and Review schema. Blogs should use Article schema. Educational institutions should explore Course and Event schema.
4. How do I know if my schema is working?
Use Google’s free Rich Results Test tool (search.google.com/test/rich-results). Paste your page URL or code, and it will show you whether your schema is valid and which rich results you are eligible for.
5. Can schema markup hurt my website?
Yes, if used incorrectly. Marking up content that is not visible to users, using misleading information, or applying the wrong schema type can lead to Google ignoring your markup or, in serious cases, applying a manual penalty. Always follow Google’s structured data guidelines.


